Reverse engineering is an innovative method that enables us to analyse and understand existing technologies, components or products and then reconstruct them in improved or optimized versions. As your reliable engineering partner, we use reverse engineering to revive existing components, optimize existing solutions, promote innovation and develop tailor-made solutions.
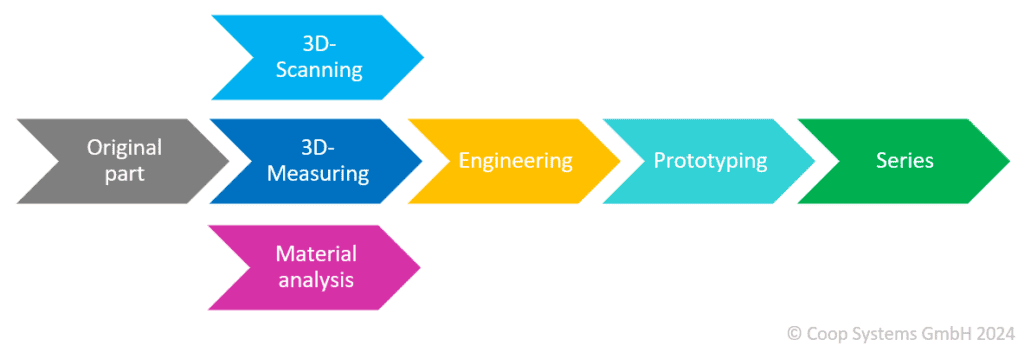
Reverse engineering in practice – a multi-stage process:
- Analyzing the existing situation:
The first step is to analyze the existing product, component or technology in detail. Both external and internal characteristics are taken into account. This may include a physical inspection, non-destructive testing, document study and interviews. - Data and information acquisition:
By using various technologies such as 3D scanners, material analysis, measuring techniques, microscopy and manual measuring tools, comprehensive data about the product is collected. Both geometric and functional aspects are recorded. - Modeling and reconstruction:
Based on the collected data, the product or component is digitally modeled and reconstructed. CAD models can be created here, which depict the exact dimensions and shapes of the original. 3D scanning is used to create point clouds and, initially, CAD raw data. Only manual post-processing produces high-quality CAD data that can be used for toolmaking, for example. - Analysis and optimization:
The reconstructed model is analyzed to identify weaknesses, opportunities for improvement or innovative adjustments. This step enables us to optimize the product, increase performance features or eliminate errors. - Prototype production:
If required, prototypes are produced based on the reconstructed model. These prototypes are used to test functionality, check design changes and evaluate the feasibility of optimizations. Suitable methods for producing prototypes include 3D printers, the vacuum casting process or simple pre-production tools. We are happy to provide our customers with comprehensive advice on this and suggest a process. - Documentation:
Comprehensive documentation takes place throughout the entire process. This includes not only the technical data and models, but also information about the reverse engineering process itself. The documentation is important for traceability, quality assurance and any future adjustments. The documentation also includes final drawings, specifications and CAD data, the data status of which is thus frozen. - Implementation & series production:
After successful analysis, reconstruction and optimization, the reconstructed product or component can be transferred to production. We usually also supply our customers with the series parts following the reverse engineering process.
Examples of already reconstructed components:
- Functional injection molded parts for the automotive industry
- Extruded seals for doors, windows, luggage compartments etc.
- Edge protection profiles
- Bellows
- Hoses & molded hoses
- Molded rubber parts (e.g. rubber grommets, molded seals)
- Rubber-metal parts (e.g. dampers)
- Bending-stamping parts
- Milled parts & turned parts
- Assemblies
Our reverse engineering services:
- Analysis of existing products:
We start with a detailed examination of an existing product or component. This can include anything from mechanical components to complex electronic systems. - Technological capture:
Using state-of-the-art technologies such as 3D scanners and advanced analysis techniques, we capture precise data on the shape, structure, color and function of the existing part. - Detailed reconstruction:
Based on the captured data, we create a detailed digital reconstruction of the part. This enables us to develop exact copies or optimized versions. - Optimization and innovation:
The reverse engineering process not only enables reproduction, but also opens up the possibility of optimization.
We can improve the product to increase performance, efficiency or other desired properties.

As a rule, we offer our customers reverse engineering free of charge if there is a realistic chance of subsequently receiving the series order.
Quality assurance through backward-looking error prevention
By using reverse engineering for quality assurance, companies can optimize their products, minimize sources of error and ensure that they always meet the highest quality standards.
- In a world where precision makes all the difference, quality assurance is crucial. In the case of faulty or defective products, reverse engineering can be used to identify the causes of faults.
- By analyzing the design data, the problem can be identified and rectified to improve quality.
- By analyzing defects in existing products, companies can take steps to avoid similar defects in new products. This contributes to proactivity in quality assurance.
- When manufacturing spare parts or repairs, reverse engineering can be used to produce exact replicas and ensure that the repair or replacement meets quality standards.
- Reverse engineering enables comprehensive documentation of products and their manufacturing processes. This documentation is crucial for quality assurance and enables precise traceability.
Quick facts – Reverse Engineering
- Technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are making reverse engineering more precise and efficient.
- Often used to breathe new life into discontinued series and spare parts.
- The most important tools for reverse engineering include CAD software, 3D scanners, 3D printers, material analyzers, microscopes, hardness testers, color fans and electrical analyzers
- usually less complex than many customers would think
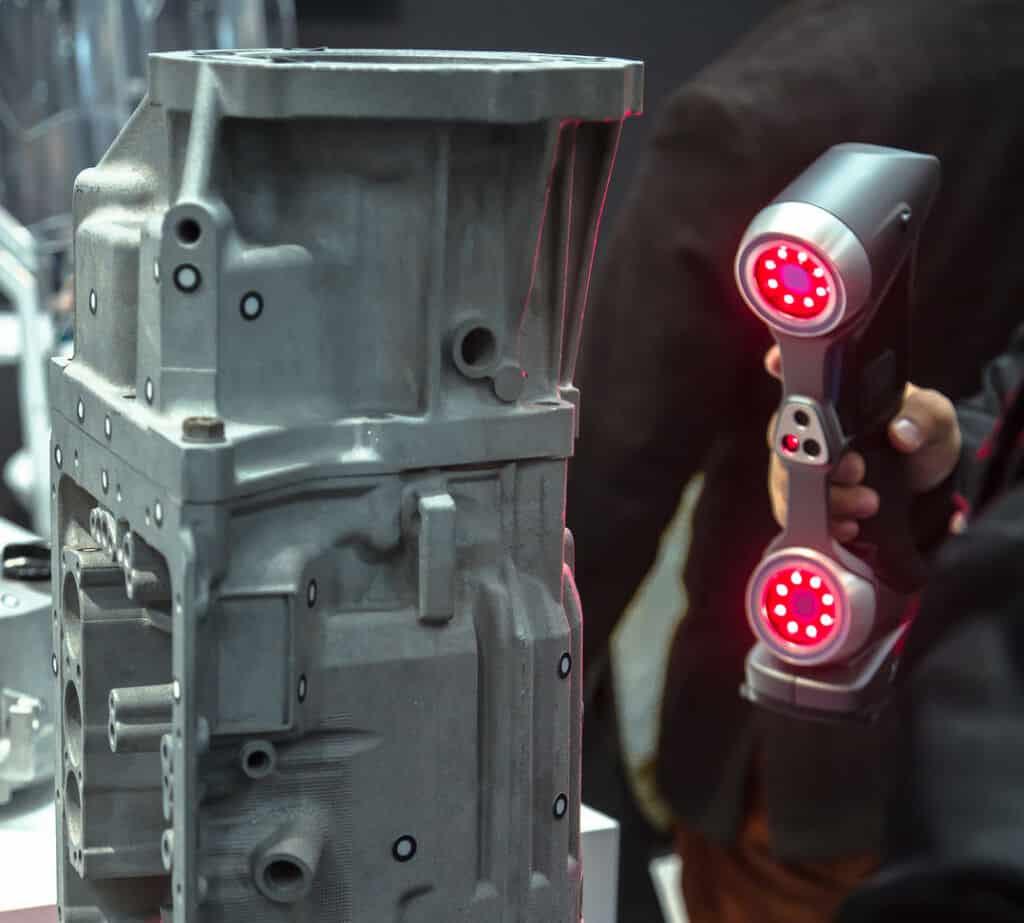
How 3D scanning works
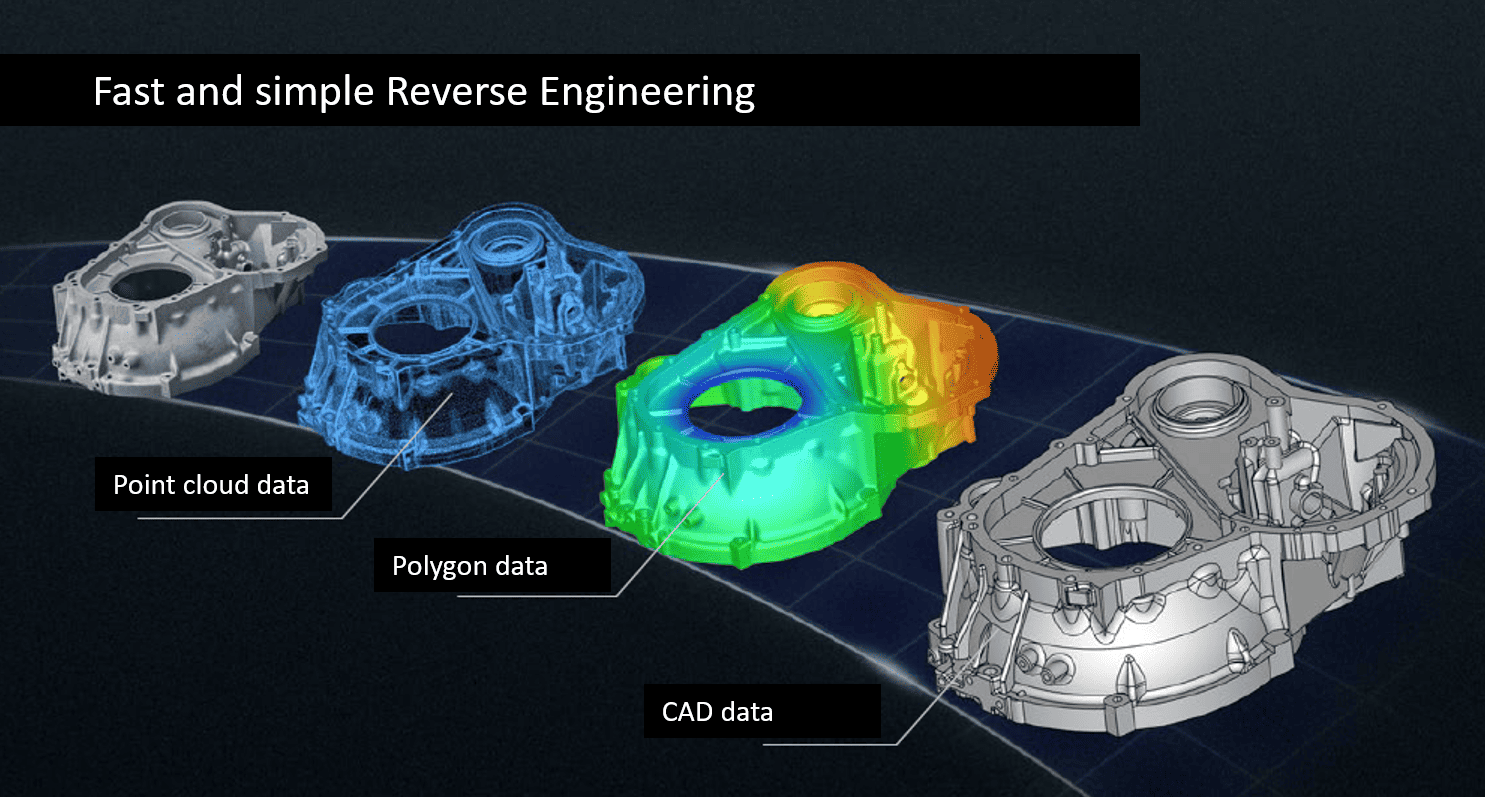
In order to provide our customers with the best possible support, our engineering office is equipped with a 3D scanner, 3D printer, a high-resolution digital microscope and a material analysis device for plastics. The 3D scan provides us with the geometry and the material analysis tells us the material of the existing component, if this is not known.
For more info:
Use our all-round service
- Personal customer advice and support
- New development, further development, cost optimization
- Creation of concept drawings, production drawings and material lists (BOM)
- Fast prototyping
- Creation of initial sample inspection reports (ISR)
- Demand-oriented production
- International serial supply
- Computer-aided process documentation
- Batch Traceability
- Continuous quality monitoring
Any more questions?
We are happy to advise you and provide you with a non-binding offer.


